Faraday's Laws of Induction
Faraday's Laws of Induction: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Production of Induced EMF for Time Varying Magnetic Flux,Production of Induced EMF by Rotating the Loop,Instantaneous Value of Induced Current in Changing Magnetic Flux, etc.
Important Questions on Faraday's Laws of Induction
According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction:
A rectangular loop and a circular loop are moving out of a uniform magnetic field to a field – free region with a constant velocity ‘v’ as shown in the figure. Explain which loop do you expect the induced emf to be constant during the passage out of the field region. The magnetic field is normal to the loops.
A circular coil of radius and turns rotates about its vertical diameter with an angular speed of in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude Find the maximum and average value of the emf induced in the coil.
A metal disc is made to spin at revolutions per second about an axis passing through its centre and normal to its plane. The disc has a radius of and spins in a uniform magnetic field of , which is parallel to the axis of rotation. Calculate
(a) The area swept out per second by the radius of the disc,
(b) The flux cut per second by a radius of the disc,
(c) The induced emf in the disc.
Say some uses of Faraday's electromagnetic induction in day to day life.
A circular coil of turns of wire has an enclosed area of per turn. It is kept perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction and rotated by about a diameter perpendicular to the field in . How much charge will pass when the coil is connected to a galvanometer with a combined resistance of ?
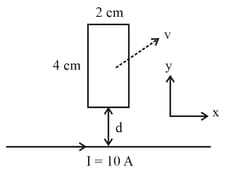
A rectangular conducting loop of length and width is in the -plane, as shown in the figure. It is being moved away from a thin and long conducting wire along the direction with a constant speed . The wire is carrying a steady current in the positive -direction. A current of flows through the loop when it is at a distance from the wire. If the resistance of the loop is , then the value of is _____ .
[Given: The permeability of free space ]
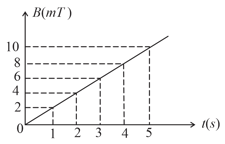
The magnetic field B crossing normally a square metallic plate of area is changing with time as shown in figure. The magnitude of induced emf in the plate during to , is _____ .
An insulated copper wire of turns is wrapped around a wooden cylindrical core of the cross-sectional area . The two ends of the wire are connected to a resistor. The total resistance in the circuit is . If an externally applied uniform magnetic field in the core along its axis changes from in one direction to in the opposite direction, the charge flowing through a point in the circuit during the change of magnetic field will be _____ .
A conducting circular loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field of with its plane perpendicular to the field. Somehow, the radius of the loop starts expanding at a constant rate of . The magnitude of induced emf in the loop at an instant when the radius of the loop is will be _______ .
A square loop of side is placed inside a long solenoid that has turns per centimetre and carries a sinusoidally varying current of amplitude and angular frequency . The central axes of the loop and solenoid coincide. The amplitude of the emf induced in the loop is . The value of is ___________
Take,
The induced emf can be produced in a coil by
A. moving the coil with uniform speed inside uniform magnetic field
B. moving the coil with non uniform speed inside uniform magnetic field
C. rotating the coil inside the uniform magnetic field
D. changing the area of the coil inside the uniform magnetic field
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A circular coil of one turn of radius is rotated about a diameter with a constant angular speed of revolutions per minute. A uniform magnetic field exists in a direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Find the average of the square of emf induced in the coil over one time period
A circular ring is placed in magnetic field of . Suddenly, its radius starts shrinking at the rate of . Find the induced emf in the ring at .
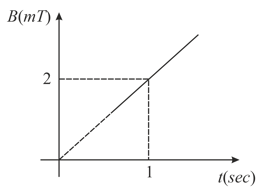
Variation of magnetic field through a coil of area is shown in figure. What is the EMF induced in the coil (in )?
A rectangular coil of two turns having arearotates in a uniform magnetic field with angular speed about an axis perpendicular to the field and in plane of the coil. If initially the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field, then the average induced emf when it has rotated through is is
A circular coil of turns has radius . It is placed with its plane perpendicular to a magnetic field of . If the magnetic field reduces to in , Calculate the e.m.f. induced in the coil.
If a conductor is moved in a direction parallel to the magnetic field, no induced current will be developed in the conductor?
The magnetic flux through a circuit carrying a current of is weber. If the current reduces to in, the induced emf be.
A rectangular coil of turns each having an area , hangs in a vertical plane with its perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of . If it is rotated by in , find the induced emf in the coil.
